The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) – sometimes called Industry 4.0 – is radically changing how businesses, especially industrial companies, operate.
Definition:
Let’s begin with a short IIoT definition: The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the vast number of machines and devices – or ‘things’ – a business uses that are now connected to the Internet. Protecting this critical operational data, secure IIoT forms a closed, private Internet network where the devices can communicate and share data with other people, systems, and things. This data can be used to improve existing work practices and business processes as well as creating entirely new ways of doing things.
Benefits of IIoT:
As IIoT devices become smaller, cheaper and smarter, they can be applied almost everywhere. The data they create can be turned into actionable insight that delivers incredible business benefits including:
Improved operational efficiency
Industrial IoT software allows you to create environments of connected assets that bring a wide range of operational efficiency benefits. Sensors located in production systems, assembly lines, warehouses and vehicles produce data that helps managers monitor exactly how an asset is performing and address issues before they arise.
Increased productivity
Industrial IoT solutions provide real-time information on the performance of equipment and people to help streamline and improve business processes and workflows.
Cost reduction
Deploying IIoT offers large cost saving benefits for organizations. For example, industrial IoT devices can save dramatically on energy bills – by as much as 70% on lighting and 30% on airconditioning, according to some estimates.
Enhanced customer experience
By placing industrial IoT sensors within products, manufacturers are able to capture and analyze data on how customers actually use their products – enabling them to improve future product upgrades and releases.
Reduced waste
Inventory management is one of the most important benefits of IIoT software. By attaching IIoT devices to products, warehouses and vehicles you can make the entire supply chain process more effective, reducing the need for excess inventory and the potential for stock-outs.
Challenges of IIoT:

Many organizations have been attracted by the benefits of industrial internet of things but realizing those benefits is not straightforward. There are many industrial IoT challenges to overcome before an organization can institute a successful IIoT program. These include:
Industrial IoT Security
- Security is one the biggest challenges for IIoT adoption. Many devices are collecting extremely sensitive data but, in many cases, the devices have been designed with little thought to security. Industrial IoT security must ensure that the identity of every person, system and thing on the network is properly managed and detected.
Data Privacy
- As more and more devices are connected to the Internet, concerns surrounding how personal and sensitive data are captured, transmitted and stored also grow. The value of IIoT lies in the ability to access, integrate, and analyze this data while maintaining data privacy.
Industrial IoT Standards
- Standards lie at the heart of the development and adoption of IIoT. Today, there are many IIoT standards but little standardization. For example, IIoT devices use a variety of methods to connect and share data, including LTE, LP-WAN, wi-fi, Bluetooth, satellite and even Ethernet when connected directly to a network.
Data Management
- Handling the volume and velocity of data being created by industrial IoT devices is a significant challenge for every organization. All this IIoT data must be collected, stored and analyzed before it can be turned into actionable insight that can drive improved decision-making.
Deployment Models
- According to PTC, 62% of IIoT deployments are on-premise, while 38% are in the cloud. The vast amounts of IIoT data being created places greater pressure on delivering flexible and scalable capacity. For industrial IoT, a cloud deployment offers performance and security gains over on-premise solutions. Hybrid industrial IoT cloud deployment – splitting processing between internal systems and the cloud – is a fast-growing deployment model for many businesses.
Range of IIoT Devices
- IIoT has many different components and there are many different types of industrial IoT devices. Typically, industrial IoT device examples include sensors, actuators, tags, beacons and receivers. When creating an IIoT network, all these devices have to be effectively and securely integrated to derive the full value of your IIoT investments.
IIoT Protocol:
Of the many different protocols Message Queue Telemetry Transport (MQTT) complements all the necessities of IoT. With a view to meet the Industry 4.0 demands, Messung now offers NX-ERA, the complete industrial automation solution to connect your business to IoT universe. All of our NX-ERA products now support MQTT.
When updating the firmware of the PLC to the latest version and using MasterTool IEC XE version 3.20, all the NX-ERA PLCs could make your business closer to Industry 4.0.
Why MQTT?

It is a lightweight message protocol that is based on subscription-publishing model and requires low bandwidth. E.g.: Facebook uses MQTT for its messenger product on mobile platform, to ensure usage of this application is minimized.
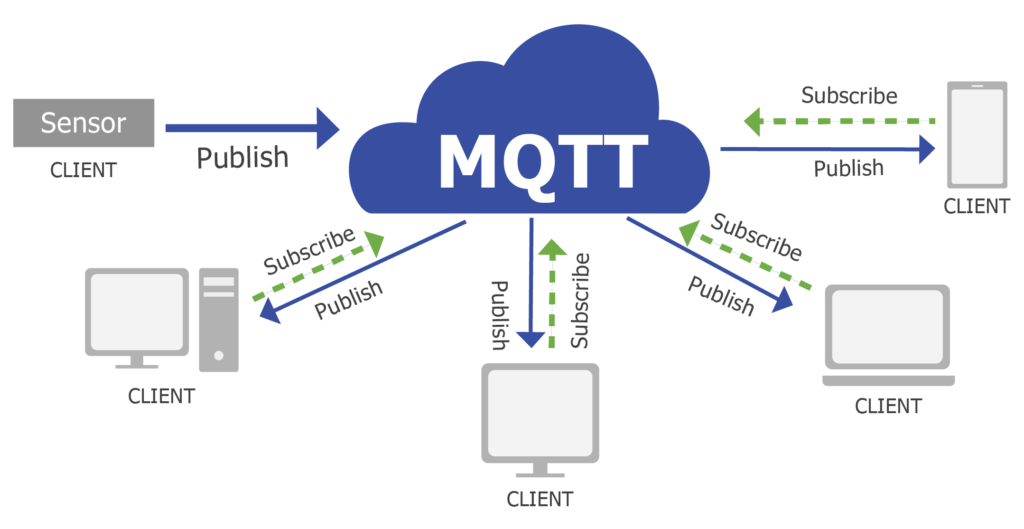
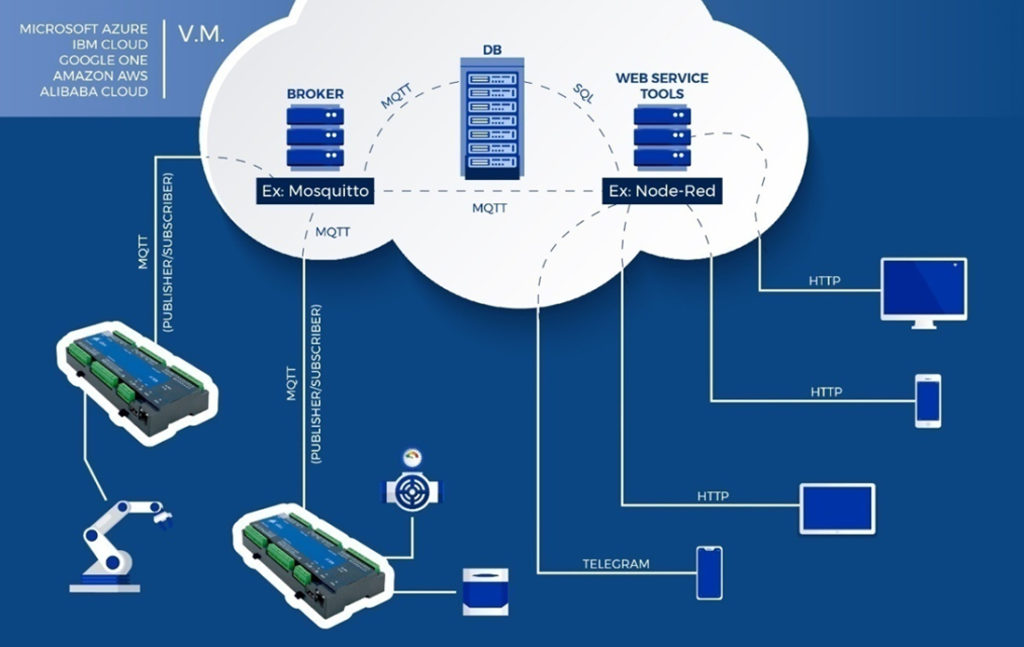
- This model follows/defines two entities in the network: the broker (also called server) and the clients.
- Using our MasterTool programmer, the user will be able to transform our PLC into a client, thereby allowing from a simple TCP / IP connection to a secure connection based on TLS certificates.
MQTT is a high-level architecture and consists of two main parts (Broker & Clients)
Broker:
- As can be seen, this protocol does not require synchronization between the parties involved, as the broker is responsible for ensuring the delivery of published messages.
- So, broker helps to sort the information and better manage the messages.
- Types of brokers available are Eclipse IoT Mosquito, Active MQ, Hive MQ etc.
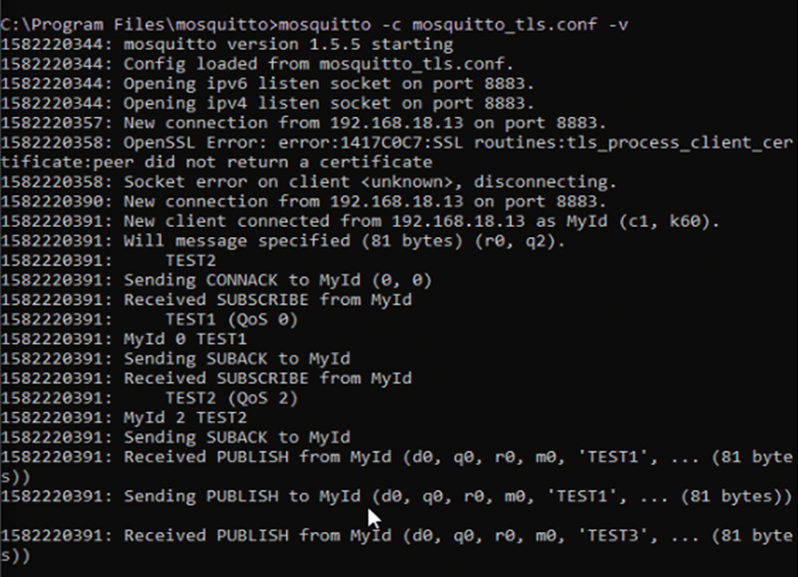
Clients:
- Clients are any devices (PLC in our case) which interact with broker; either publishing messages or subscribing to a topic.
- Topics are the routes where messages are published within a broker.
- When PLC publishes message to the broker; and broker forwards this message to subscribers avoiding point-to-point connections between subscribers and publishers.
- When broker (server) publishes any message, then PLC (client) acts as a subscriber.
- MQTT supports TLS (Transport Security Level) for secure connection between client & server. Communication between client and server is established via TCP connection or an encrypted TLS connection for secure messages.
Web Service Tools
- Any web service tool could be used as a programming platform for intuitive and straightforward integration between smart devices, PLCs and brokers. Node-Red is an example of the web server tool.
- If we write or publish a message from Node-Red, this published message will be received by broker first. If PLC is subscribed to this message under any topic, then it will receive the message from the broker.
- Thus, it is possible to communicate with different cloud platforms, such as Node-RED®, where it is possible to create supervision diagrams for an entire system, including different devices.
SCREEN DISPLAY ON MOBILE/TERMINAL/TABLET through CLOUD PLATFORM/LOCAL SERVER
TYPICAL ARCHITECTURE

Our customer is an Automotive Ancillary Manufacturing company having a huge installed base of PLCs (of different make) in their premises being utilized for varied applications including Robotic Cells.
Customer Requirement
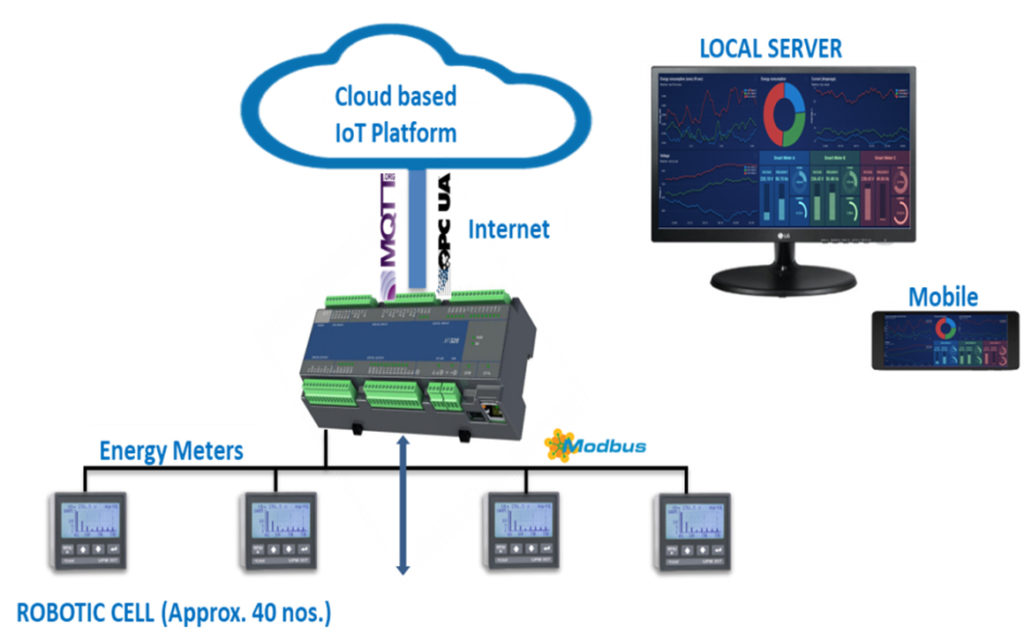
Application: Robot Line Welding Machine
The customer wanted his PRODUCTION data and some critical alarms to be monitored on Web Visualisation tool and to collect the data centrally in a local Server. Also to be energy efficient, the customer wanted to monitor energy consumed at each stage of the production line.
Proposed Solution:
Since the existing PLC does not support Industry 4.0 compatibility, Messung suggested a cost effective solution to retrofit the PLC with latest NX-ERA XPRESS PLC which has integrated multiple protocol communication including MQTT & OPC UA protocols.
To take care of Energy Management System, energy meters were installed with Modbus RTU communication facility. The NX-ERA XPRESS PLC gathered the data from the energy meters on integrated MODBUS Protocol (inbuilt RS485 port). Moreover the data was compiled and sent to the Customer Server.
The application was developed, panel rewired and monitored within an hour. What’s more, this task was accomplished during the break, so it helped to reduce machine downtime.
The data was taken on TCP/IP port to the Customer Server on MQTT with broker running on the same.
Production Management Solution:
Monitoring & Data Recording

Messung NX-ERA PLCs for Industrial Automation have opened new doors to ever increasing demands for Internet of Things by introducing MQTT, where the users can operate, make analysis and even save on their existing sensors, devices or even machines.
Also, users can check, monitor and even control some of the critical functionalities of any machine in the plant at their fingertips on their interactive devices based on operating systems like MAC OS, Windows, IOS or Androids.
As proven automation experts and leading PLC supplier in India, Messung has in-depth understanding of industrial machinery, production processes and practical implementation of technology, complemented by a strong team of experienced engineers with tried and tested execution methodology. Messung’s cutting-edge industrial automation & control solutions with IIoT can transform operations and efficiencies across the shop floor.
